Alphabet Soup: Acronyms you need to know
Ever read an article, have a conversation, or watch a news program that includes myriad acronyms that cause a “what does that mean” moment? Get some answers by reviewing the compilation of acronyms below.
Ever read an article, have a conversation, or watch a news program that includes myriad acronyms that cause a “what does that mean” moment? Get some answers by reviewing the compilation of acronyms below.
APM: Alternative Payment Model. APMs are a type of payment reform incorporating quality and total cost of care into reimbursement rather than a traditional fee-for-service structure. Eligible clinicians who successfully participate in a CMS-defined Advanced APM may be exempted from MIPS reporting (see below) and receive a five percent incentive payment.
CBO: Congressional Budget Office. CBO produces independent analyses of budgetary and economic issues to support the Congressional budget process. CBO “scores” proposed bills to help lawmakers understand the cost or savings associated with a legislative package.
CHHC: Congressional Hearing Health Caucus. CHHC is a bipartisan caucus of members from the U.S. House and Senate committed to supporting the needs of people with hearing loss and other auditory disorders. The AAO-HNS is a member of the Friends of the CHHC.
CMS: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. CMS is a federal agency within the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. It is responsible for administrating the Medicare program and working with states on administrating their Medicaid programs.
EHDI: Early Hearing Detection & Intervention. EHDI is a critical program that supports statewide plans identifying infants/children with hearing loss and directing them to early intervention services. The AAO-HNS is working with the hearing health community to advance legislation in the 115th Congress to reauthorize the federal portion of the EHDI program for an additional five years.
HIT: Health Information Technology. Software and computer systems now make medical records electronic, reducing paperwork and redundant forms. Federal and state governments are implementing numerous proposals to encourage the adoption of HIT, while promoting quality initiatives and protecting patient privacy.
MACRA: Medicare Access and the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) Reauthorization Act. MACRA repealed the Sustainable Growth Rate (SGR) formula that Medicare previously used to determine physician reimbursement. The program comprises two tracks: Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) and the Advanced Alternative Payment Model (APM).
MedPAC: Medicare Payment Advisory Commission. MedPAC is an independent federal body established by the Balanced Budget Act of 1997, responsible for advising Congress on topics within the Medicare program, and more specifically, on issues dealing with payments to private health plans participating in Medicare and health providers that serve Medicare beneficiaries.
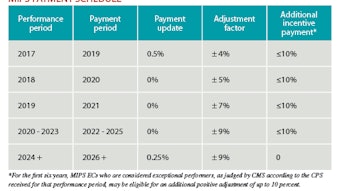
MIPS: Merit-based Incentive Payment System. MACRA created the MIPS to replace the current CMS Quality Initiative Programs. MIPS incorporates aspects of several CMS quality programs into a component score to determine physician payment. Eligible clinicians will report on three categories that will add up to a composite performance score (CPS).
NAM: National Academy of Medicine. NAM was established in 1970 as the Institute of Medicine (IOM) and works to address crucial issues in health, medicine, and policy. In June 2016, NAM published “Hearing Healthcare: Priorities for Improving Access and Affordability,” which highlights the importance of easier access and more affordable options for hearing healthcare. The AAO-HNS submitted comments to NAM prior to the report’s release.
NIDCD: National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders. NIDCD is one of 27 Centers and Institutes that make up the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and conducts biomedical and behavioral research in the fields of hearing, taste, smell, voice, balance, language, and speech, supporting disease prevention and health promotion.
PAC: Political Action Committee. PACs allow individuals with shared interests the opportunity to pool their voluntary donations to make contributions to federal candidates on behalf of the entire group. PACs represent a legal and ethical way to participate in the election process. ENT PAC (www.entpac.org) is the political action committee of the AAO-HNS.
PCAST: President’s Council of Advisors on Science and Technology. PCAST is an advisory group of the nation’s leading scientists and engineers who directly advise the President and the Executive Office of the President. In 2015, PCAST released the report, “Aging America & Hearing Loss: Imperative of Improved Hearing Technologies.”
TIA: Truth in Advertising. The AAO-HNS and others in the physician community support state and federal efforts to implement TIA legislation requiring ALL healthcare providers to inform patients of their credentials and/or level of training in patient communications and marketing materials. TIA is an important component to providing patients with the best possible care.